Godot 4.5 has been released, marking another major milestone for the community with contributions from over 400 developers and nearly 2,500 commits. This update places a strong emphasis on accessibility while continuing to expand the engine's capabilities. Highlights include long-awaited stencil buffer support for advanced rendering techniques, a new shader baker for pre-compiling shaders, powerful debugging tools, and accessibility enhancements such as screen reader integration and improved localization for multilingual projects.
Below is a summary of the new features in this release:
Rendering and shaders
Among the most anticipated additions is stencil buffer support, available across all rendering backends and enabling developers to implement new techniques that take advantage of depth information.
Shader workflows have also been improved. The shader editor UI has been reorganized for better usability, and direct rendering enhancements include ambient specular occlusion, SMAA support, and bent normal maps.
A new shader baker is available in the project exporter. When enabled, all shaders are pre-compiled at export time, ensuring that players will not experience long shader compilation times when running the game.
Motion vectors, previously exclusive to the Forward+ renderer, are now available in the Mobile renderer.
Additional rendering capabilities include new StandardMaterial properties, giving developers more control over FPS-style objects positioned close to the camera, such as hands, weapons, and tools.
Fire effect implemented entirely with StandardMaterial3D.
Support for fragment density maps has also been introduced, and the Mobile renderer has been optimized with explicit half-precision floating-point (FP16) usage.
The cull mask system has been overhauled for Lights, Decals, and Particle Colliders, and a fix has been applied to LightmapGI to resolve shadow leak issues.
Finally, a set of performance optimizations completes the rendering improvements.
GUI
Godot 4.5 fully integrates AccessKit, a library that provides a cross-platform, cross-language layer for implementing accessibility in custom UI toolkits. With this integration, screen readers and other assistive technologies are now supported.
The rendering of default controls and the editor UI has been reworked to ensure they appear sharp on HiDPI screens, fixing previous blurriness.
Foldable containers have been added, allowing developers to create dynamically cascading GUI objects with the ability to toggle whether contents are expanded. This eliminates the need for previous workarounds to achieve the same effect.
Control node behavior has been improved with new recursive properties for mouse and focus handling. Developers can now enable or disable focus_behavior_recursive and mouse_behavior_recursive on a container, automatically affecting all child controls. This simplifies complex GUIs, such as inventory screens, where parts of the interface should remain inactive until certain conditions are met, without requiring custom messaging or manual management of individual controls.
Support for OEM Alt code input has been added in TextEdit and LineEdit.
Label rendering has also been enhanced, with stackable outlines and a new paragraph separation theme property for RichTextLabel, providing more control over text appearance.
Additionally, oversampling can now be configured per viewport, replacing the previous global setting.
Core
The core of the engine has received several improvements. Script backtracing support for GDScript and C# has been added, allowing developers to see backtraces of runtime errors directly in their logs. This makes it possible to debug and fix issues that occur during testing or in shipped titles.
The behavior of the Resource.duplicate() method has been improved to increase predictability and reliability. Together with the new Resource.duplicate_deep() method, developers now have full control over what gets duplicated, including arrays, dictionaries, and nested resources.
Additional changes include a new Node.get_orphan_node_ids() method, improvements to Node.print_orphan_nodes(), and the addition of a scene_changed signal to the SceneTree.
Thread safety has been added to Object signals, and internal nodes are no longer duplicated.
The String::num_scientific() function now uses the Grisu2 algorithm for more reliable serialization.
Finally, a complete build profile feature has been introduced to better detect options that can be disabled, reducing binary size.
Internationalization
This release adds the ability to preview translations directly in the editor, allowing developers to see how their projects will appear to end-users in different languages. It is also now possible to swap languages on the fly within the editor, enabling developers to preview and test multiple language options in a single session.
Audio / Video
In the audio and video area, developers can now seek within Theora video files. The multi-channel audio resampler has been improved, eliminating crackling issues in videos with six or more channels. Additionally, it is now possible to add metadata tags to WAV and OGG audio streams.
Animation
On the 3D side, a new BoneConstraint3D class has been added, enabling one bone to be bound to another. This opens the door to creating more natural movements and poses in character rigs.
The animation editor has also received several usability improvements. Developers can now move and scale selections directly within the bezier editor, making it easier to adjust multiple points at once. A new option allows automatic tangents for newly created Bezier points, streamlining the workflow.
The animation player has also been improved with the ability to sort animations alphabetically, helping developers keep large projects organized. In addition, animation filtering has been introduced, addressing one of the most requested features by the community.
C#
For C#, NativeAOT is now supported on Android, allowing compilation directly to a device's native code and removing the need for the .NET runtime. This results in significantly faster startup times and smaller memory footprints, which is especially beneficial for mobile devices. In addition, a preload hook has been added to load .NET assemblies from the APK, and assemblies can now also be loaded directly from PCK files.
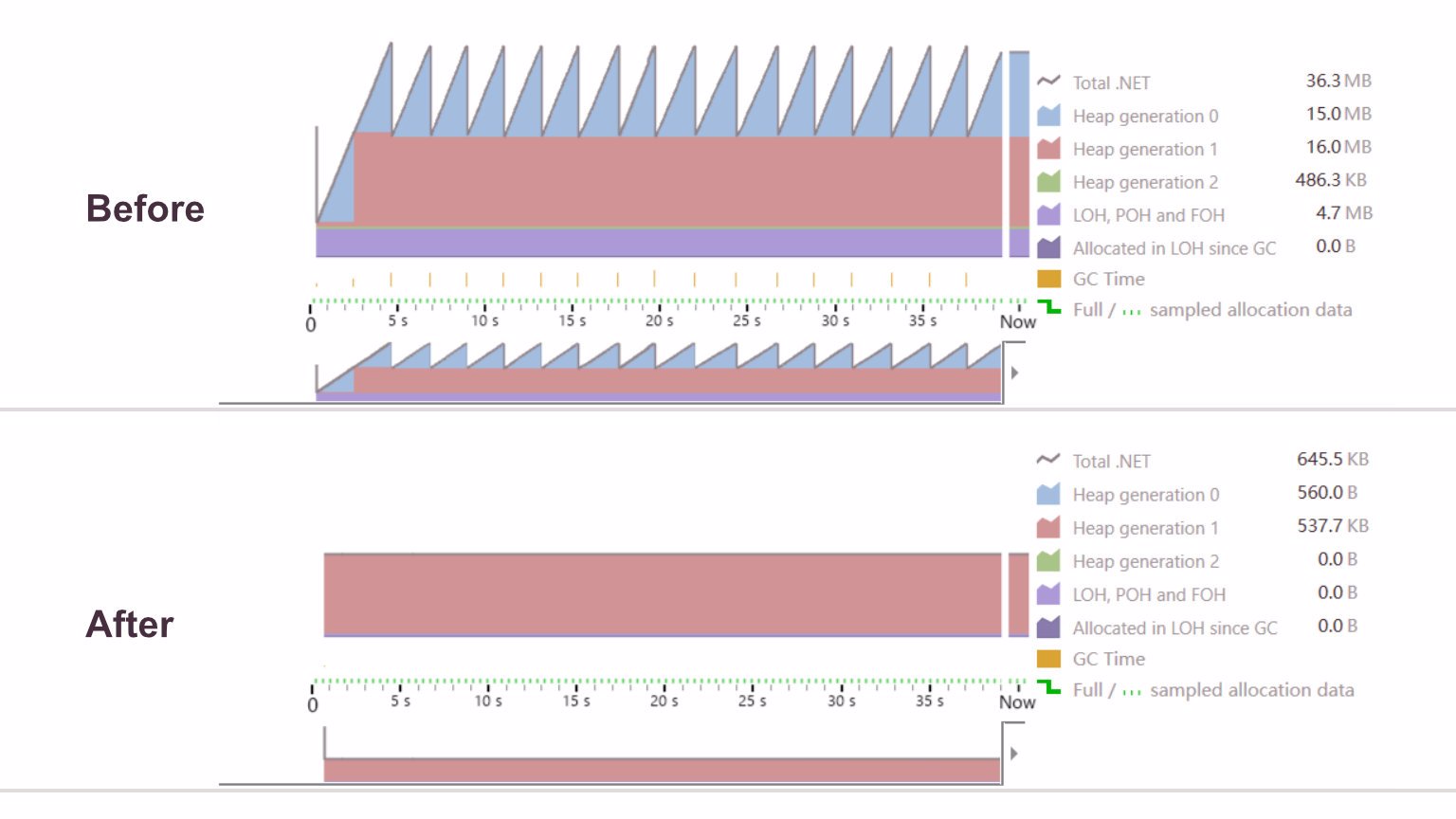
Performance has also been improved through optimizations to proxy object creation when the engine invokes a C# script. This can reduce memory usage by up to 60x.
Documentation
In the documentation, a new required qualifier has been added for virtual methods. This allows developers to quickly see whether a virtual method provides a default implementation or if overriding it is mandatory when extending a class.
Editor
Named EditorScripts are now available in the command palette, providing a centralized way to run project-specific commands.
Exported variables can now be of type Variant without requiring an initial value. The editor allows developers to assign any compatible Variant type, with a type selector that adjusts the input widget automatically.
Editor customization has been expanded with the ability to override settings on a per-project basis and toggle sections in the Inspector. The resource workflow is also more flexible, with support for dropping preload resources as UIDs and a new Paste as Unique option in the editor resource picker.
In the Game view, a convenient Mute Game toggle has been introduced, and multiple remote nodes can now be selected at runtime.
Particles2D has gained emission shape gizmos for clearer visualization, and drag and drop into array property editors has been improved.
A dedicated Duplicate button has been added to the Project Manager, making it easy for developers to back up an existing project or create a new fork.
In the editor, signal connection settings now include a new Append Source option. When enabled, the source object is appended immediately after the original arguments of the signal.
Finally, the Video RAM Profiler now supports meshes, and script documentation can be searched without requiring manual recompilation.
GDScript
A new @abstract annotation has been added for classes, preventing direct instantiation. The annotation can also be applied to functions, marking them for explicit override by child classes.
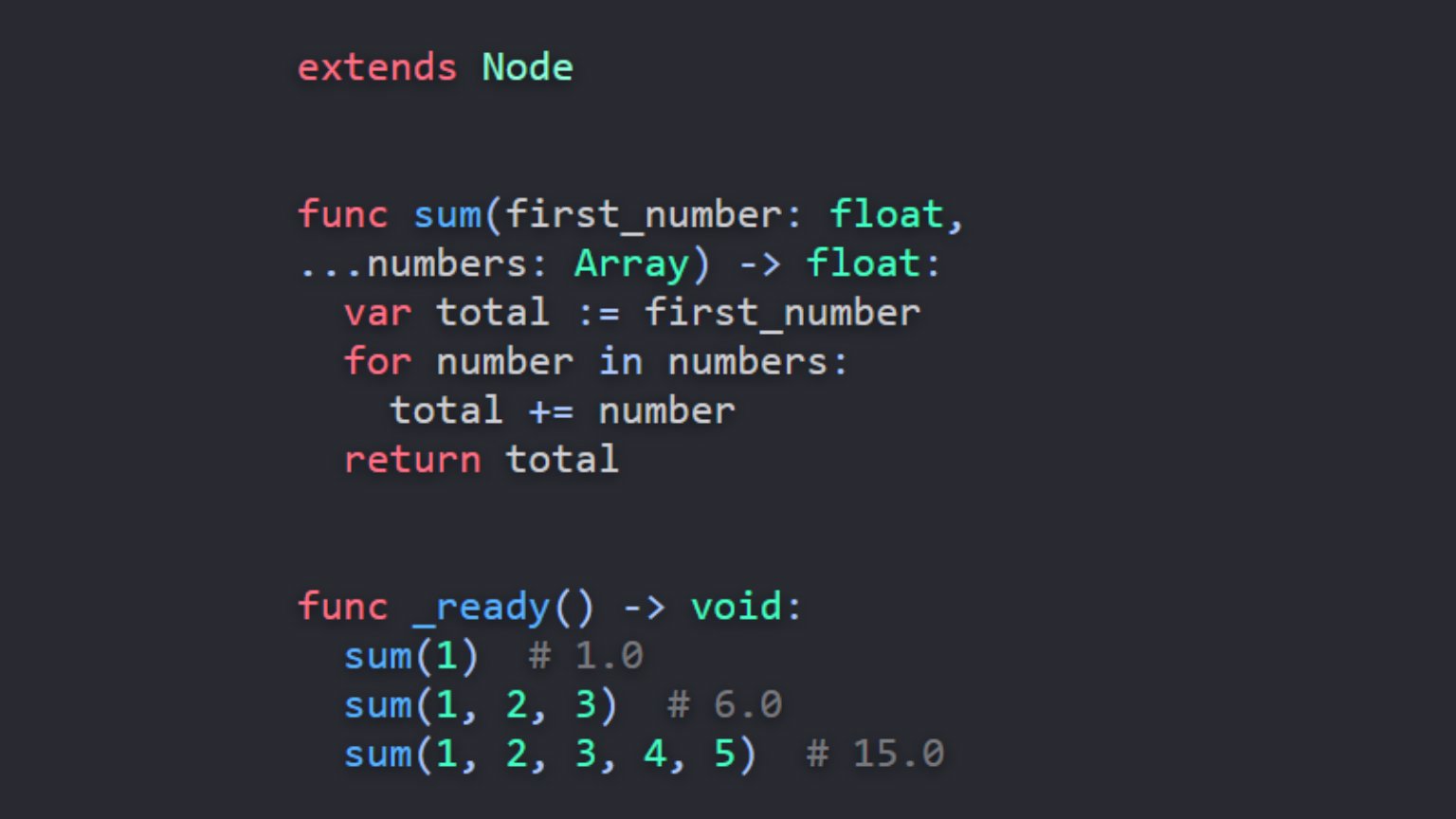
Variadic arguments are now supported, allowing functions to accept a flexible number of input parameters. This allows turning the final argument of a function into an array that is called as if it were a sequence.
The script editor has seen several usability improvements. Code editing now includes inline color pickers and clearer highlighting for warning lines.
Autocompletion has been expanded to support @export_tool_button and overridden user-defined methods, while script members are highlighted consistently alongside native ones.
The editor no longer adds parentheses when a Callable is expected, resulting in more accurate autocompleted code.
GDExtension
Main loop callbacks can now be registered directly from GDExtension, allowing developers to run code at engine-specific events such as startup and shutdown. This resolves previous issues with accessing engine singletons and supports ongoing efforts to integrate C#/.NET with GDExtension, including the ability to register frame callbacks.
Import
Godot 4.5 reintroduces the ability to batch edit multiple 3D assets, allowing developers to assign an external material to all of them through options in the Import dock.
The ResourceImporterTexture now includes Channel Remap settings, and scripts can be attached to nodes directly from the Advanced Import Settings dialog.
Extracted meshes, materials, and animations can now be referenced using UIDs in addition to paths. JPEG compatibility and performance have also been improved with the adoption of libjpeg-turbo.
Navigation
A dedicated 2D navigation server has been introduced. Previously, NavigationServer2D relied on 3D navigation logic constrained to two axes, requiring 3D support even for pure 2D games. With the new server, developers can now configure 2D and 3D navigation independently, reducing export size and providing more control over pathfinding.
Physics
The implementation of 3D fixed-timestep interpolation has been completely overhauled, with all logic now handled within the SceneTree. This improvement benefits all projects without breaking any existing APIs.
Interpolation with 10 ticks per second.
Jolt Physics, the 3D physics engine introduced in Godot 4.4, has received nearly 20 fixes and improvements, enhancing stability and performance.
New functionality has been added for SoftBody3D, including the ability to apply forces and impulses, as well as support for physics interpolation. Additionally, chunk tilemap physics has been introduced.
Input
SDL3 has been integrated as the new gamepad input driver for desktop platforms. This mature library replaces the built-in “joypad” platform drivers, which were inspired by earlier versions of SDL and presented various issues.
Platforms
On the platforms side, lightmap baking and UV unwrapping are no longer limited to desktop systems. These features are now available directly on mobile devices, allowing developers to carry out the same workflows on their phone or tablet.
Android
The Android editor experience has been improved with the introduction of the TouchActionsPanel, which provides common action buttons such as save, undo, and redo. These buttons simulate actions like ui_undo and ui_redo using pre-existing shortcuts.
Support has been added for running the Godot engine within an Android Service, along with compatibility for 16 KB page sizes.
Native debug symbols generation is now enabled, and the minimum supported SDK has been raised to 24.
A new edge-to-edge export option allows developers to draw across the entire screen while keeping system bar overlays, providing a fullscreen appearance with a modern look that matches Android's design style.
Godot also now supports access to the device's raw camera feed, enabling developers to use live camera input for features such as AR or custom image processing.
Linux
Progress has been made toward full Wayland support, a modern replacement for the X11 protocol. In this release, native sub-windows have been implemented, allowing developers to take advantage of multi-window output. The next step will be to enable in-editor game window embedding to achieve full parity with the X11 version of the editor.
macOS
In-editor embedding of the game window, a feature introduced in Godot 4.4, has now been implemented on macOS. In addition, the ANGLE OpenGL ES compatibility layer has been switched to the Metal backend.
Web
Web platform performance has received a significant boost in this release due to a change in a single compiler flag. This results in universal improvements for both web applications and the editor workflow.
visionOS
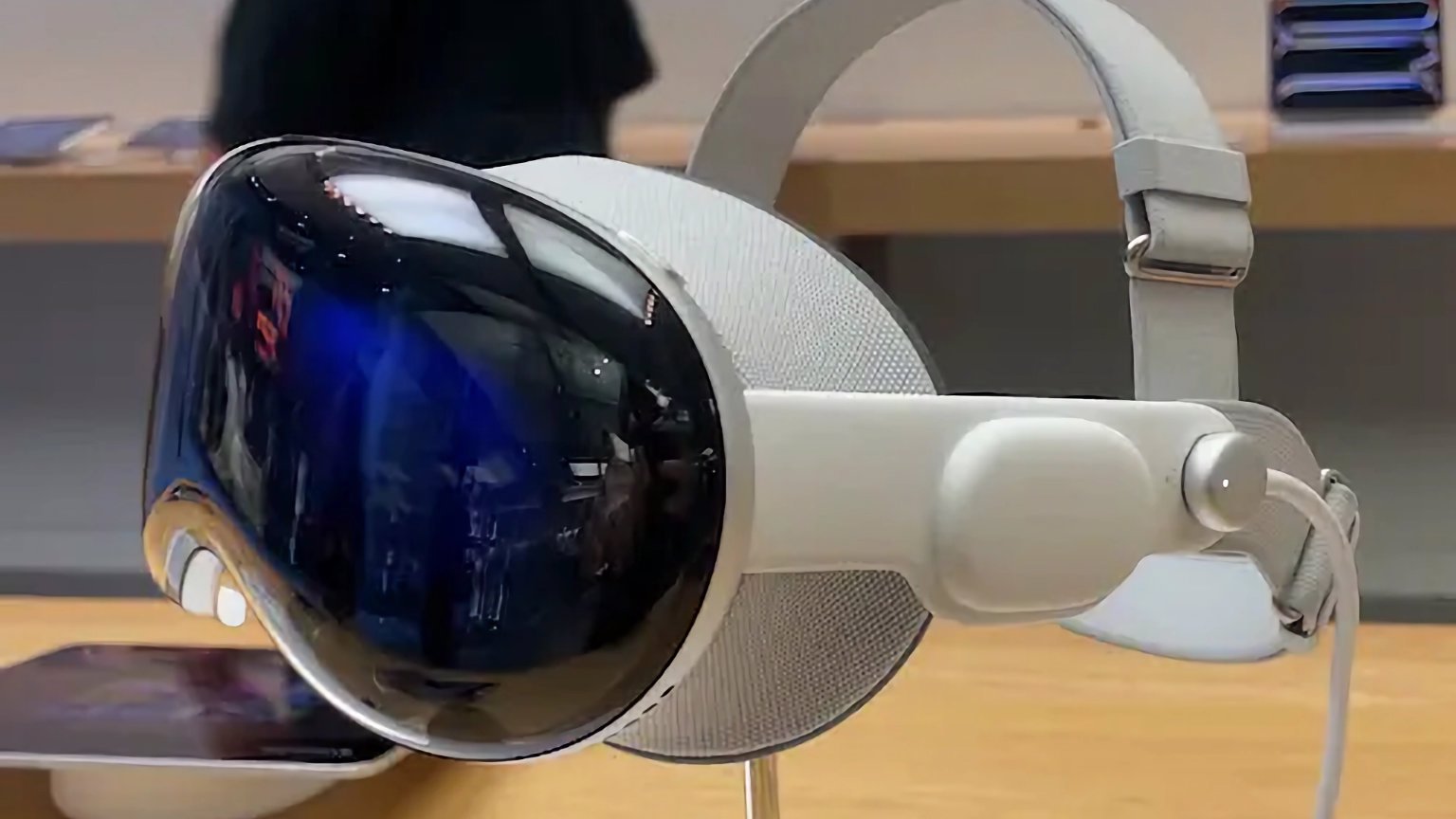
Godot now supports exporting projects to Apple's XR platform, visionOS, making them compatible with the Apple Vision Pro. Godot 4.5 introduces the first step of visionOS integration, thanks to contributions from Apple's visionOS engineering team. Currently, projects can be exported as “windowed apps,” which appear as floating windows in the user's 3D space, with fully immersive experiences planned for future updates.

Windows
Godot 4.5 drops support for Windows 7 and 8.1. This change helps clean up the codebase and allows for the integration of more modern APIs in Windows builds.
The Windows export pipeline has also been improved. Developers can now modify the metadata of Windows binaries without using the third-party rcedit tool. This enables setting a custom icon, as well as updating product name, company information, and other metadata, fully out of the box and from any platform.
Additionally, the visible border in WINDOW_MODE_FULLSCREEN has been removed by setting the window region. Official Windows binaries are now signed with a new code signing certificate provided by Prehensile Tales.
XR
Extended reality support has been expanded with the addition of Direct3D 12. Implementations of fragment density maps and motion vectors for the Mobile renderer also improve rendering and provide a foundation for supporting more XR extensions.
Support has been added for the XR_EXT_render_model and XR_EXT_interaction_render_model extensions in OpenXR. These provide access to fully animated models of the controllers held by the user, enabling devices like Meta Quest 3S and Pico 4 Ultra to display their controllers without additional developer setup.
Foveated rendering is now supported on the Vulkan Mobile renderer via the Fragment Density Map extension. This technique renders the center of the viewport at full resolution while reducing detail in the periphery, improving performance for standalone VR headsets.
Support for Application SpaceWarp is now available through the OpenXR vendors plugin. Application SpaceWarp uses frame synthesis to allow rendering at half rate while the GPU synthesizes the next frame, which can free up compute time on mobile headsets.
For more information, be sure to visit the official Godot Engine website.




