Blender, the popular free and open-source 3D creation suite, has received a significant new update. This is a Long Term Support (LTS) release, making it ideal for long-term projects by providing two years of updates and bug fixes.
Maintaining the previous release's focus on stability, this version delivers nearly 500 bug fixes alongside a broad range of new features and enhancements.
One of the most notable changes is full support for the Vulkan backend, which now reaches feature parity with OpenGL, with users being encouraged to try the backend by enabling it in the application's preferences.
Another major area of improvement is Geometry Nodes, which introduces numerous new and updated nodes. These include support for importing a variety of file formats such as CSV (.csv), Stanford PLY (.ply), OpenVDB (.vdb), STL (.stl), Wavefront (.obj), and plain text (.txt). In addition, custom mesh normals can now be edited using the new Set Mesh Normal node, which supports both the traditional "Tangent Space" normals and a new, faster "Free" format. Further new nodes improve data access, string handling, and Grease Pencil geometry workflows.
All new Geometry Nodes in Blender 4.5 LTS
With this update, Blender should feel faster and snappier, thanks to performance improvements like faster texture loading, quicker startup times, and multi-threaded shader compilation enabled by default on supported platforms.
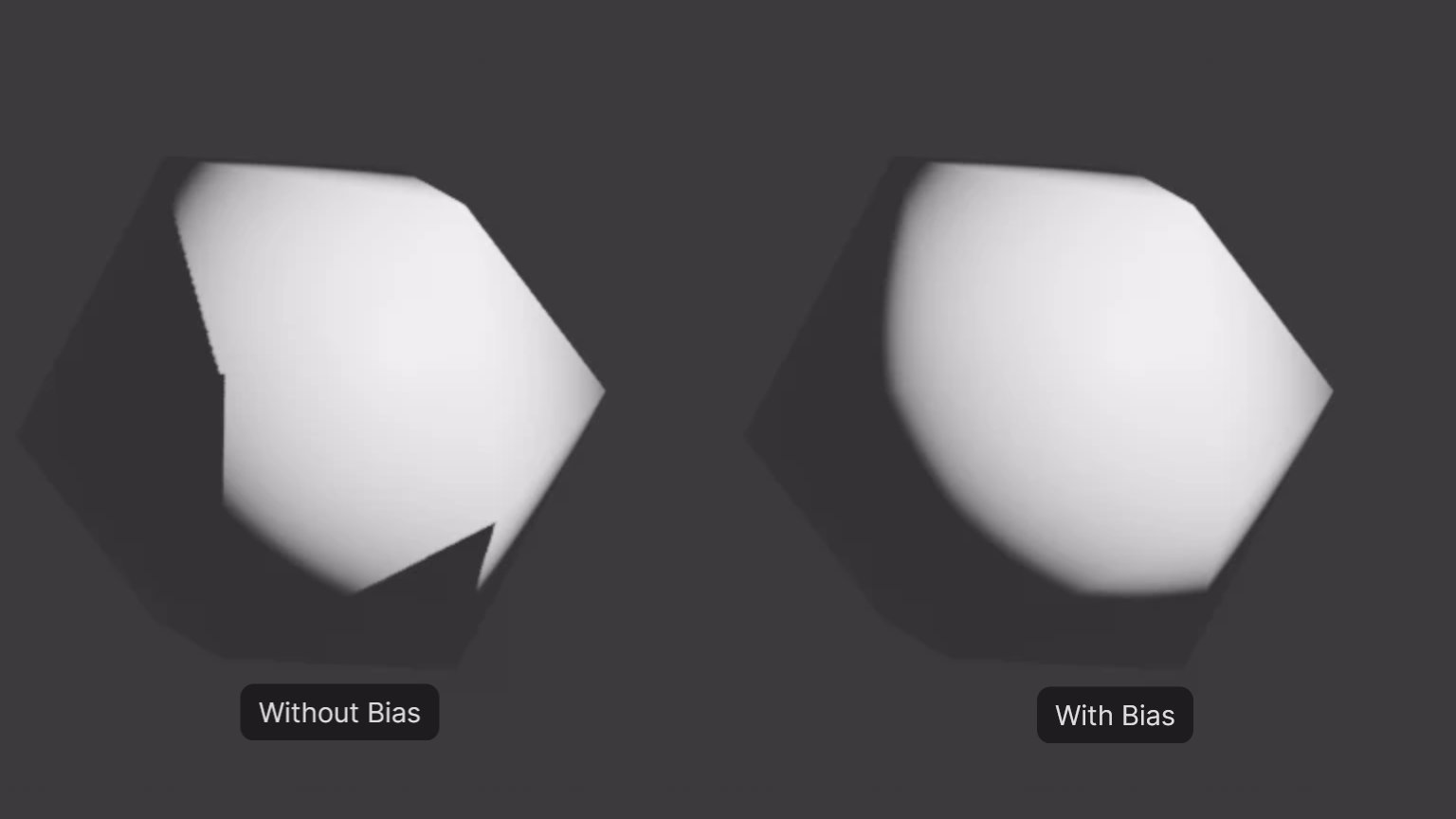
The EEVEE renderer adds a feature first introduced in Cycles back in Blender 3.0: shadow terminator bias. This per-object setting helps reduce self-shadowing artifacts on low-polygon geometry by shifting the shadowed position along the shading normal.

The Compositor has also been significantly improved. All procedural texture nodes from Shaders and Geometry Nodes are now available, and the system is more unified, with common nodes being added and easily copied across Shader and Geometry Node setups. It also introduces several new nodes for image workflows, including Image Info, Relative to Pixel, and Image Coordinates, along with a long list of other improvements.
Blender 4.5 LTS compositor meets procedural textures.
Grease Pencil sees several key improvements in this update, including integration with the Compositor, support for Geometry Nodes tools, and the return of previously missing features. A new render pass outputs visible Grease Pencil strokes and fills into a separate layer, making it easier to isolate, enhance, or apply effects to Grease Pencil elements during compositing.
Additionally, Grease Pencil rendering can now be disabled per View Layer using the Filter option, similar to how it works for Surfaces, Volumes, and other data types. A new supersampling anti-aliasing (SSAA) method also improves line quality, resulting in smoother strokes.
Grease pencil render pass.
In UV editing, UVs are now visible across all object modes in the Image Editor's Mask and Paint views. Previously, this visibility was limited to Edit Mode. The visibility and opacity of UVs can now be controlled through the Overlays popover.
A new object type, called Point Cloud, has been introduced to represent large numbers of individual points in 3D space. This type is ideal for visualizing 3D scan data, particle simulations, or sparse datasets, and offers significantly better performance compared to using regular meshes.
On the modeling front, the standout improvement is the updated Grid Fill operator, described as feeling “like magic.” It can now replace or correct existing geometry, in addition to filling holes as before. This makes it ideal for cleaning up areas with poor topology, replacing them with a fresh, smooth grid of quads.
In painting modes such as Sculpt, Vertex Paint, and Texture Paint, there is now support for randomizing hue, saturation, and value, either across the entire stroke or on a per-stroke basis, adding a natural, varied look to strokes without extra effort. Sculpt mode also benefits from a new, faster solver for the Trim tools. Called Manifold (as it works best on manifold geometry), this new method is significantly faster than the previous Fast mode, which has now been renamed to Float.
Trimming in Sculpt mode is now orders of magnitude faster on manifold meshes.
Finally, the user interface continues to receive refinements, making it more polished, intuitive, and customizable. Notable improvements include easier placement of nodes into frames, the ability to hide tabs in the Properties Editor (useful for customizing the workspace), and better asset management in both the Asset Browser and File Browser.
This overview highlights the key updates in this release. For a detailed list of all new features, be sure to visit the official release page on Blender's website.




